Leveraging the Semantic Layer for Business Success: A Practical Guide
In today's data-driven business landscape, organizations are inundated with vast amounts of information. The challenge lies not in collecting data, but in making it meaningful, accessible, and actionable across the enterprise. This is where the semantic layer comes into play, serving as a crucial bridge between raw data and business intelligence. Let's explore how practitioners can effectively implement and utilize the semantic layer to drive tangible business outcomes.
Understanding the Semantic Layer
The semantic layer is a comprehensive framework that translates complex data structures into business-friendly terms and concepts. It comprises several key components, each serving a specific purpose in enhancing data understanding and utilization.
Key Components and Their Roles
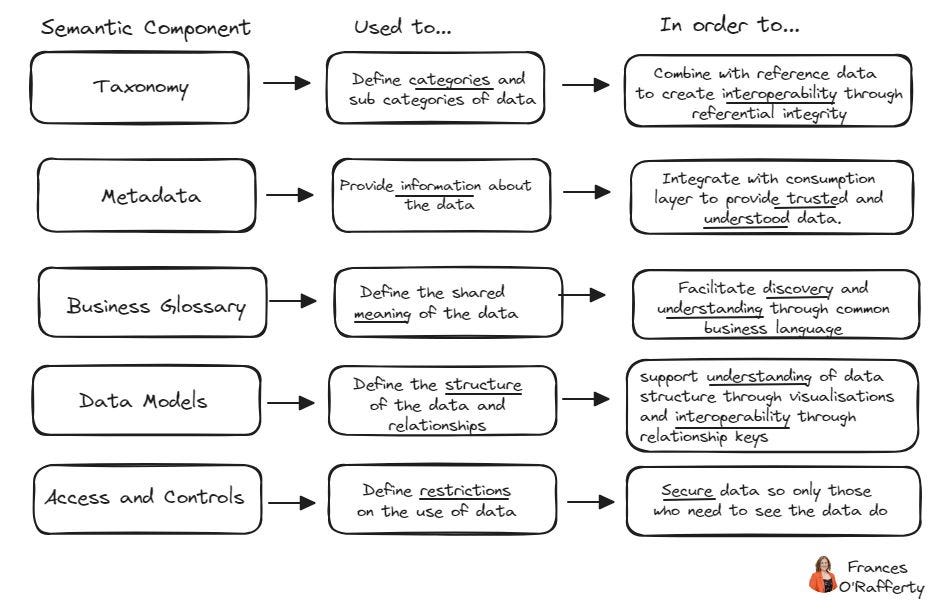
Taxonomy: Categorizes data, enabling interoperability
Metadata: Provides context about the data
Business Glossary: Defines shared meanings of data elements
Data Models: Illustrates data structures and relationships
Access and Controls: Manages data security and permissions
Practical Implementation Strategies
1. Start with a Solid Taxonomy
Begin by creating a robust taxonomy that categorizes your data. This forms the foundation for interoperability and consistent data interpretation across departments.
Practical Tip: Involve stakeholders from different business units when creating your taxonomy to ensure it covers all relevant aspects of your business.
2. Enrich with Detailed Metadata
Metadata is crucial for providing context to your data. Implement a systematic approach to metadata management.
Practical Tip: Use automated tools to extract and manage metadata, ensuring it's always up-to-date and comprehensive.
3. Develop a Comprehensive Business Glossary
A well-maintained business glossary ensures everyone speaks the same language when it comes to data.
Practical Tip: Regularly review and update your business glossary, and make it easily accessible to all employees through a centralized platform.
4. Create Intuitive Data Models
Data models help visualize complex relationships and structures within your data.
Practical Tip: Use visual data modeling tools and ensure your models are documented and shared widely within the organization.
5. Implement Robust Access Controls
Ensuring data security is paramount. Implement granular access controls to protect sensitive information.
Practical Tip: Regularly audit access permissions and use role-based access control (RBAC) to simplify management.
Real-World Business Example: RetailCo's Transformation
Let's consider RetailCo, a mid-sized retail chain struggling with data silos and inconsistent reporting across its 500 stores.
The Challenge
RetailCo's marketing, sales, and inventory management teams were working with different definitions of key metrics like "customer lifetime value" and "stock turnover rate." This led to conflicting reports and inefficient decision-making.
The Solution
RetailCo implemented a semantic layer with the following approach:
Taxonomy: Created a hierarchical structure categorizing data into areas like "Customer," "Product," "Sales," and "Inventory."
Metadata: Implemented automated metadata extraction from their various data sources, providing clear lineage and quality metrics for each dataset.
Business Glossary: Developed a company-wide glossary defining terms like "active customer" and "fast-moving items" consistently across all departments.
Data Models: Created visual data models showing the relationships between customers, purchases, and inventory, making it easier for non-technical staff to understand data structures.
Access Controls: Implemented role-based access, ensuring store managers could only access data relevant to their location, while regional managers had broader views.
The Outcome
Within six months of implementing the semantic layer:
Report discrepancies decreased by 85%
Time spent on data reconciliation reduced by 70%
Cross-departmental collaboration on data-driven initiatives increased by 50%
Customer satisfaction improved by 15% due to more personalized marketing and better inventory management
Key Takeaways for Practitioners
Start Small, Scale Fast: Begin with a pilot project in one department, then expand based on lessons learned.
Prioritize User Adoption: Invest in training and change management to ensure widespread use of the semantic layer.
Iterate Continuously: Treat your semantic layer as a living entity, continuously refining and expanding it based on business needs.
Leverage Technology: Utilize modern data catalog and governance tools to automate and streamline semantic layer management.
Measure Impact: Regularly assess the impact of your semantic layer on key business metrics to demonstrate value and secure ongoing support.
By thoughtfully implementing a semantic layer, organizations can transform their data from a complex puzzle into a clear, actionable asset. This not only improves operational efficiency but also empowers employees at all levels to make data-driven decisions confidently, ultimately driving business success in our increasingly data-centric world.
Tools for Semantic Layer Implementation:
Data Catalog and Metadata Management: • Apache Atlas (Open Source) • Amundsen (Open Source) • DataHub (Open Source) • Azure Purview (Paid, with some free features)
Business Glossary: • Collibra Community Edition (Free version) • Alation Data Dictionary (Free trial available) • Azure Purview (Includes business glossary features)
Data Modeling: • draw.io (Free) • ERDPlus (Free)
Taxonomy Management: • PoolParty Free (Basic features) • VocBench (Open Source)
Access Control and Security: • Keycloak (Open Source) • OpenIAM Community Edition (Open Source)
Data Governance Platforms: • Apache Griffin (Open Source) • ODPi Egeria (Open Source) • Azure Purview (Comprehensive data governance)
Visualization and Reporting: • Metabase (Open Source) • Apache Superset (Open Source)
ETL and Data Integration: • Talend Open Studio (Open Source) • Apache NiFi (Open Source)
Data Quality and Validation: • Great Expectations (Open Source) • Azure Purview (Includes data quality features)
All-in-One Cloud Solutions: • Azure Purview (Comprehensive data governance and management)
Azure Purview deserves special mention because it offers a comprehensive suite of tools that cover multiple aspects of the semantic layer, including data discovery, data catalog, data map, data lineage, and sensitive data classification. While it's not free, it provides a robust solution for organizations already invested in the Microsoft Azure ecosystem.